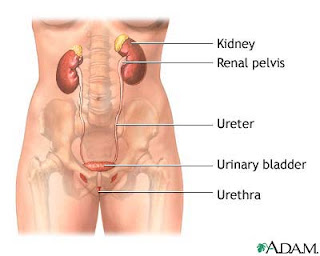
 A urinary tract infection is an infection that can happen anywhere along the urinary tract. When it affects the lower urinary tract it is known as a simple cystitis (a bladder infection) and when it affects the upper urinary tract it is known as pyelonephritis (a kidney infection).
A urinary tract infection is an infection that can happen anywhere along the urinary tract. When it affects the lower urinary tract it is known as a simple cystitis (a bladder infection) and when it affects the upper urinary tract it is known as pyelonephritis (a kidney infection).
UTIs are diagnosed usually by isolating and identifying the urinary pathogen from the patient; there are some home tests available for presumptive diagnosis.
The most common cause of UTIs are bacteria from the bowel that live on the skin near the rectum or in the vagina, which can spread and enter the urinary tract through the urethra. Once these bacteria enter the urethra, they travel upward, causing infection in the bladder and sometimes other parts of the urinary tract.
Symptoms
May have an infection if have any of these symptoms:
- Feel pain or burning when urinate.
- Feel like have to urinate often, but not much urine comes out when do.
- Belly feels tender or heavy.
- Urine is cloudy or smells bad.
- Have pain on one side of the back under ribs. This is where kidneys are.
- Have fever and chills.
- Have nausea and vomiting.
7 Nursing Diagnosis for UTI
1. Acute pain
related to:
inflammation and infection of the urethra, bladder and other urinary tract structures.
2. Hyperthermia
related to:
inflammatory reaction
3. Impaired Urinary Elimination
related to:
frequent urination, urgency and hesistancy
4. Risk for Fluid Volume Deficit
related to:
excessive evaporation and vomiting
5. Disturbed Sleep Pattern
related to:
pain and nocturia
6. Imbalanced Nutrition, Less Than Body Requirements
related to:
anorexia
7. Anxiety
related to:
crisis situations, coping mechanisms are ineffective
8. Knowledge Deficit: about condition, prognosis, and treatment needs
related to:
lack of sources of information.